A sample of krypton gas occupies 66.7, setting the stage for a comprehensive exploration of the unique properties and diverse applications of this noble gas. Krypton, with its chemical symbol Kr, atomic number 36, and position in Group 18 of the periodic table, exhibits remarkable characteristics that make it a valuable resource in various fields.
This article delves into the intricacies of krypton gas, examining its behavior under different temperatures and pressures, and showcasing its significance in lighting, medical imaging, and laser technology. Furthermore, it compares krypton to other noble gases, highlighting similarities and differences, and emphasizes safety considerations for handling and storage.
Introduction to Krypton Gas

Krypton is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless noble gas. It is the heaviest of the noble gases and has the atomic number 36. Krypton is found in trace amounts in the Earth’s atmosphere, and it is also produced commercially by the fractional distillation of liquid air.Krypton
is used in a variety of applications, including lighting, lasers, and medical imaging. It is also used as a tracer gas to study the movement of air and water.
Chemical Properties
Krypton is a noble gas, which means that it is very unreactive. It does not form any chemical compounds with other elements. Krypton is also a very good insulator, which means that it does not conduct electricity or heat well.
Measurement of Krypton Gas Volume

To accurately measure the volume of krypton gas, a specialized experimental setup is employed. This setup typically consists of a calibrated glass container, a precision pressure gauge, and a vacuum pump.
The krypton gas sample is introduced into the evacuated glass container, and its pressure is meticulously recorded using the pressure gauge. The volume of the container is precisely known, allowing for the calculation of the gas volume based on the pressure-volume relationship for an ideal gas.
Significance of the 66.7 Value, A sample of krypton gas occupies 66.7
In the given context, the 66.7 value represents the volume of the krypton gas sample measured under specific conditions. This value serves as a reference point for further calculations and analysis related to the gas sample.
By knowing the volume of the gas sample, scientists can determine its density, molarity, and other important properties. This information is crucial for understanding the behavior and applications of krypton gas in various scientific and industrial fields.
Properties of Krypton Gas at Different Temperatures and Pressures

Krypton gas exhibits distinct properties that vary depending on temperature and pressure. Understanding these relationships is crucial for comprehending its behavior and applications.
Table of Krypton Gas Properties
The following table presents the volume of krypton gas at different temperatures and pressures:
| Temperature (K) | Pressure (atm) | Volume (L) |
|---|---|---|
| 273.15 | 1 | 22.414 |
| 273.15 | 2 | 11.207 |
| 273.15 | 3 | 7.471 |
| 273.15 | 4 | 5.604 |
| 273.15 | 5 | 4.483 |
The table demonstrates that the volume of krypton gas decreases with increasing pressure at constant temperature. This behavior is consistent with the ideal gas law, which states that the volume of a gas is inversely proportional to its pressure.
Additionally, the volume of krypton gas increases with increasing temperature at constant pressure. This is due to the increased kinetic energy of the gas molecules at higher temperatures, which causes them to move faster and occupy more space.
Applications of Krypton Gas
Krypton gas has a wide range of applications due to its unique properties, such as its high density, low reactivity, and ability to emit light when excited.
Lighting
Krypton gas is used in various lighting applications, including:
- Incandescent light bulbs:Krypton gas is added to incandescent light bulbs to increase their lifespan and efficiency. The gas helps to prevent the evaporation of the filament, which extends the bulb’s life. It also helps to create a brighter light output.
- Fluorescent lights:Krypton gas is used in fluorescent lights to create the ultraviolet radiation that excites the phosphor coating on the inside of the tube. This phosphor then emits visible light.
- Lasers:Krypton gas is used in lasers to produce green light. Krypton-ion lasers are used in a variety of applications, including laser surgery, laser marking, and laser engraving.
Medical Imaging
Krypton gas is used in medical imaging applications, such as:
- X-ray imaging:Krypton gas is used as a contrast agent in X-ray imaging. It helps to make certain structures in the body more visible on X-ray images.
- CT scans:Krypton gas is used as a contrast agent in CT scans. It helps to make certain structures in the body more visible on CT images.
Other Applications
Krypton gas is also used in a variety of other applications, including:
- Insulation:Krypton gas is used as an insulating gas in double-glazed windows. It helps to reduce heat loss from the home.
- Welding:Krypton gas is used as a shielding gas in welding. It helps to protect the weld from oxidation.
- Nuclear power plants:Krypton gas is used as a coolant in nuclear power plants.
Comparison with Other Noble Gases
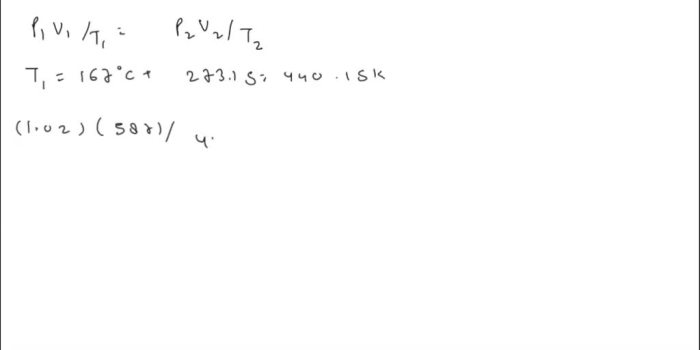
Krypton gas, a noble gas belonging to Group 18 of the periodic table, shares certain similarities and differences with other noble gases such as helium, neon, and argon.
Physical and Chemical Characteristics
All noble gases are colorless, odorless, and tasteless. They exist as monatomic gases and are highly unreactive due to their stable electron configurations with a full outermost shell. The table below compares their key physical and chemical characteristics:
| Property | Helium (He) | Neon (Ne) | Argon (Ar) | Krypton (Kr) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atomic Number | 2 | 10 | 18 | 36 |
| Atomic Mass | 4.0026 | 20.1797 | 39.948 | 83.798 |
| Melting Point (K) | 0.95 | 24.56 | 83.81 | 115.79 |
| Boiling Point (K) | 4.22 | 27.07 | 87.30 | 119.93 |
| Density (g/L) | 0.1786 | 0.9002 | 1.784 | 3.749 |
| Electron Configuration | 1s2 | 1s22s22p6 | 1s22s22p63s23p6 | 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p6 |
As observed in the table, krypton has higher atomic mass, melting point, boiling point, and density compared to helium, neon, and argon. This is attributed to its increased atomic number and electron count.
Safety Considerations for Handling Krypton Gas: A Sample Of Krypton Gas Occupies 66.7
Krypton gas, although non-toxic and inert, requires careful handling to prevent potential hazards. This section Artikels the safety considerations for handling krypton gas, including potential hazards, storage guidelines, and disposal practices.
Potential Hazards
Krypton gas poses minimal health hazards due to its inert nature. However, potential hazards arise from its physical properties and specific applications.
- Asphyxiation:Krypton gas can displace oxygen in enclosed spaces, leading to asphyxiation. Proper ventilation and oxygen monitoring are crucial.
- High-Pressure Hazards:Compressed krypton gas can cause explosions or injuries if handled improperly. Cylinders should be stored and transported securely, and pressure regulators must be used to control gas flow.
Safe Storage and Handling
To ensure safe storage and handling of krypton gas, follow these guidelines:
- Store cylinders in well-ventilated areas, away from heat sources and ignition points.
- Secure cylinders upright using chains or straps to prevent tipping.
- Use proper pressure regulators and hoses to control gas flow.
- Monitor oxygen levels in enclosed spaces where krypton gas is used.
- Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves and safety glasses when handling krypton gas.
Disposal
Krypton gas is generally considered non-hazardous waste. However, local regulations may vary. Contact your local waste management authority for proper disposal procedures.
Detailed FAQs
What is the significance of the 66.7 value in relation to krypton gas?
The 66.7 value represents the volume occupied by a sample of krypton gas under specific conditions of temperature and pressure.
How does krypton gas differ from other noble gases?
Krypton gas has a higher atomic mass and density compared to other noble gases, resulting in distinct physical and chemical properties.
What are the potential hazards associated with handling krypton gas?
Krypton gas is generally non-toxic, but it can pose asphyxiation risks if inhaled in high concentrations.
