Safety and body mechanics chapter 7 – In the realm of occupational health and safety, Chapter 7: Safety and Body Mechanics holds immense significance, providing a comprehensive understanding of the principles and practices that underpin injury prevention and workplace well-being. This chapter delves into the fundamentals of body mechanics, exploring the intricate relationship between posture, movement, and the prevention of musculoskeletal disorders.
By examining common body mechanics errors and their potential consequences, individuals can gain valuable insights into the importance of adopting proper techniques in everyday activities, reducing the risk of injuries and enhancing overall physical well-being.
Principles of Body Mechanics: Safety And Body Mechanics Chapter 7

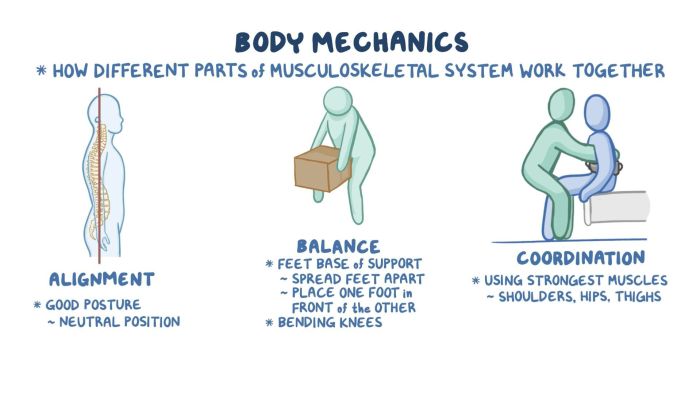
Body mechanics refers to the proper alignment and movement of the body to maintain optimal posture, prevent injuries, and maximize efficiency during everyday activities. It involves understanding the principles of leverage, balance, and coordination to ensure that the body is in a neutral position, minimizing stress on muscles, joints, and ligaments.
Proper body mechanics is essential for preventing injuries, as it helps distribute forces evenly throughout the body, reducing the risk of sprains, strains, and other musculoskeletal issues. It also promotes good posture, which can improve overall health and well-being.
Common Body Mechanics Errors
Common body mechanics errors that can lead to injuries include:
- Slouching:Poor posture where the shoulders are rounded, the head is forward, and the back is curved.
- Lifting with a rounded back:Bending over to lift heavy objects instead of squatting and lifting with the legs.
- Twisting the body while lifting:Turning the body while lifting heavy objects, putting stress on the lower back.
- Carrying heavy objects on one side:Uneven distribution of weight, leading to muscle imbalances and potential injuries.
- Overreaching:Extending the body beyond its comfortable reach, straining muscles and joints.
Body Mechanics for Specific Tasks
Proper body mechanics for common tasks includes:
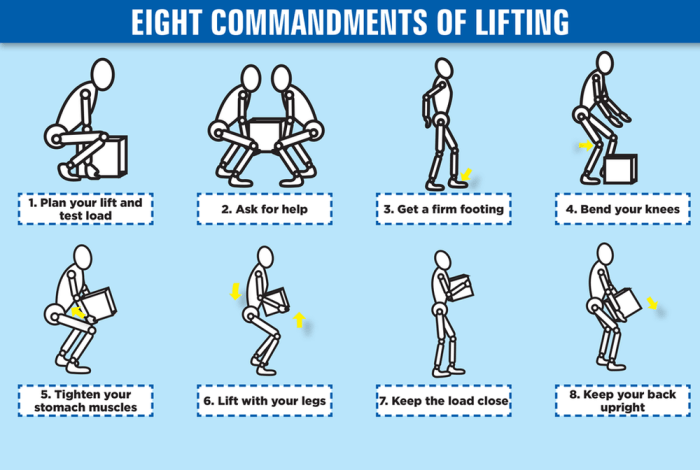
- Lifting:Squat down, keeping the back straight, and lift with the legs, not the back.
- Carrying:Distribute weight evenly on both sides of the body, hold objects close to the body, and avoid twisting.
- Pushing:Use the legs to push, keeping the back straight and avoiding excessive force.
Ergonomics and Body Mechanics, Safety and body mechanics chapter 7
Ergonomics is the science of designing and arranging workplaces to optimize efficiency and minimize risk of injury. Ergonomic principles can be applied to improve body mechanics, such as:
- Adjustable workstations:Allowing individuals to adjust their workspaces to fit their body size and needs.
- Proper lighting:Reducing eye strain and promoting good posture.
- Regular breaks:Preventing muscle fatigue and promoting circulation.
Body Mechanics Education and Training
Body mechanics education and training are crucial for individuals and organizations to prevent injuries and promote overall well-being. Training can include:
- Classroom instruction:Teaching the principles of body mechanics and common errors.
- Practical demonstrations:Showing proper techniques for lifting, carrying, and other tasks.
- On-the-job training:Supervising individuals in the workplace to ensure proper body mechanics.
Questions and Answers
What are the key principles of body mechanics?
Body mechanics principles involve maintaining proper posture, lifting and carrying objects correctly, and using appropriate techniques to minimize strain on the body.
How can I avoid common body mechanics errors?
To prevent errors, focus on maintaining a neutral spine, bending from the knees when lifting, and avoiding twisting or overreaching.
Why is ergonomics important in body mechanics?
Ergonomics plays a crucial role by designing workplaces and equipment to fit the human body, reducing the risk of musculoskeletal disorders.