Match the principle of relative dating with its definition, a fundamental concept in geology that enables us to establish the sequence of geological events and construct a timeline of Earth’s history. By understanding the principles of superposition and cross-cutting relationships, geologists can determine the relative ages of rock layers and geological structures, providing insights into the dynamic processes that have shaped our planet.
The principle of relative dating serves as a cornerstone for unraveling the mysteries of Earth’s past, allowing us to piece together the sequence of events that have shaped our planet’s geological landscape.
Definition of the Principle of Relative Dating

The principle of relative dating is a fundamental concept in geology that allows scientists to determine the relative ages of geological formations and events. It is based on the assumption that younger layers of rock are deposited on top of older layers, and that geological features that cut across other features are younger than the features they cut across.
Concept of Superposition, Match the principle of relative dating with its definition
The concept of superposition states that in a sequence of undisturbed sedimentary rocks, the oldest layer is at the bottom and the youngest layer is at the top. This is because younger sediments are deposited on top of older sediments, and the weight of the younger sediments compacts and hardens the older sediments.
Concept of Cross-Cutting Relationships
The concept of cross-cutting relationships states that a geological feature that cuts across another geological feature is younger than the feature it cuts across. This is because a younger feature must have been formed after the older feature was already in place.
Examples of Relative Dating
- If a layer of sandstone is found above a layer of limestone, the sandstone is younger than the limestone.
- If a fault cuts across a layer of shale, the fault is younger than the shale.
- If a volcanic dike cuts across a layer of granite, the dike is younger than the granite.
Applications of the Principle of Relative Dating
The principle of relative dating is used to establish geological time scales and to determine the sequence of events in Earth’s history.
Establishing Geological Time Scales
Relative dating is used to create geological time scales, which are charts that show the relative ages of different rock formations and events. Geologists use a variety of techniques to establish geological time scales, including:
- Superposition
- Cross-cutting relationships
- Index fossils
- Radiometric dating
Determining the Sequence of Events
Relative dating is also used to determine the sequence of events in Earth’s history. For example, geologists can use relative dating to determine the order in which different mountain ranges were formed, or the order in which different climates existed.
Examples of Applications
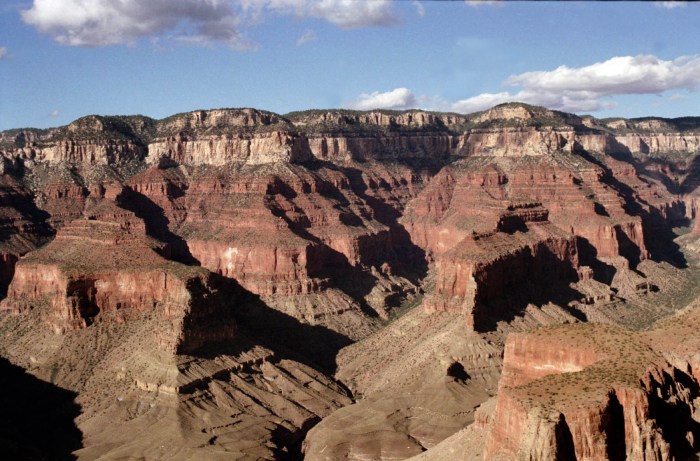
- Geologists have used relative dating to determine that the Grand Canyon was formed by the Colorado River over millions of years.
- Geologists have used relative dating to determine that the Appalachian Mountains were formed by a series of collisions between North America and other continents.
- Geologists have used relative dating to determine that the Earth has experienced several ice ages over the past million years.
Limitations of the Principle of Relative Dating

The principle of relative dating has some limitations, including:
Inability to Provide Absolute Ages
Relative dating cannot be used to determine the absolute age of a geological formation or event. It can only determine the relative ages of different formations and events.
Unconformities
Unconformities are gaps in the geological record that can make it difficult to determine the relative ages of different formations. Unconformities can be caused by erosion, non-deposition, or tectonic activity.
Other Geological Features
Other geological features, such as faults and folds, can also make it difficult to determine the relative ages of different formations. Faults can displace rocks, and folds can overturn rocks, making it difficult to determine their original order.
Examples of Limitations
- Geologists cannot use relative dating to determine the absolute age of the Grand Canyon.
- Geologists cannot use relative dating to determine the absolute age of the Appalachian Mountains.
- Geologists cannot use relative dating to determine the absolute age of the Earth’s ice ages.
Popular Questions: Match The Principle Of Relative Dating With Its Definition
What is the principle of relative dating?
The principle of relative dating is a geological concept that allows us to determine the relative ages of rock layers and geological structures based on their superposition and cross-cutting relationships.
How is the principle of relative dating used in geology?
The principle of relative dating is used to establish geological time scales and determine the sequence of events in Earth’s history. It helps geologists reconstruct past geological events and understand the dynamic processes that have shaped our planet.
What are the limitations of the principle of relative dating?
The principle of relative dating cannot provide absolute ages for geological formations. Additionally, unconformities and other geological features can complicate the interpretation of relative dating.