Molecular genetics of color mutations in pocket mice embarks on an intriguing journey, delving into the intricate interplay between genes and coat color. Pocket mice, with their diverse array of coat colors, serve as a captivating model for exploring the genetic underpinnings of color variation.
The genetic basis of color mutations in pocket mice is a complex and fascinating subject. Genes, the fundamental units of heredity, hold the blueprint for an organism’s traits, including coat color. Mutations, alterations in the DNA sequence, can disrupt these genetic instructions, leading to a wide range of color variations.
Introduction

Molecular genetics is the study of the structure and function of genes at the molecular level. Color mutations are changes in the DNA sequence that alter the expression of genes responsible for coat color. Pocket mice ( Perognathusspp.) are a group of small rodents that exhibit a wide range of color mutations, making them an ideal model for studying the genetic basis of color variation.
Genetic Basis of Color Mutations
Genes are responsible for determining the coat color of pocket mice. Different mutations in these genes can lead to changes in the production or function of proteins involved in pigment synthesis. Some common types of color mutations include albinism, which results in a lack of pigment, and melanism, which causes an increase in pigment production.
Examples of Specific Color Mutations in Pocket Mice, Molecular genetics of color mutations in pocket mice
- Albino: This mutation results in a lack of tyrosinase, an enzyme necessary for melanin production.
- Melanistic: This mutation results in an increase in melanin production, leading to a darker coat color.
- Cinnamon: This mutation affects the production of pheomelanin, resulting in a reddish-brown coat color.
Molecular Mechanisms of Color Mutations
Color mutations are caused by changes in the DNA sequence that alter the structure or function of genes. These changes can occur through various mechanisms, including:
- Point mutations: These are single-nucleotide changes that can disrupt the coding sequence of a gene.
- Insertions and deletions: These mutations involve the addition or removal of nucleotides from the DNA sequence.
- Gene rearrangements: These mutations involve the movement or duplication of large segments of DNA.
Evolutionary Implications of Color Mutations
Color mutations can have significant evolutionary implications by affecting the survival and reproduction of pocket mice. For example, albinism can reduce camouflage and increase predation risk, while melanism can provide better camouflage in certain environments. Natural selection acts on these color variations, shaping the distribution of color mutations in populations over time.
Examples of How Color Mutations Have Influenced the Evolution of Pocket Mice
- In desert environments, melanistic pocket mice have an advantage in camouflage and survival compared to lighter-colored individuals.
- In areas with high predation pressure, albino pocket mice are more vulnerable to predators and have lower reproductive success.
Applications of Molecular Genetics in Color Mutation Research: Molecular Genetics Of Color Mutations In Pocket Mice
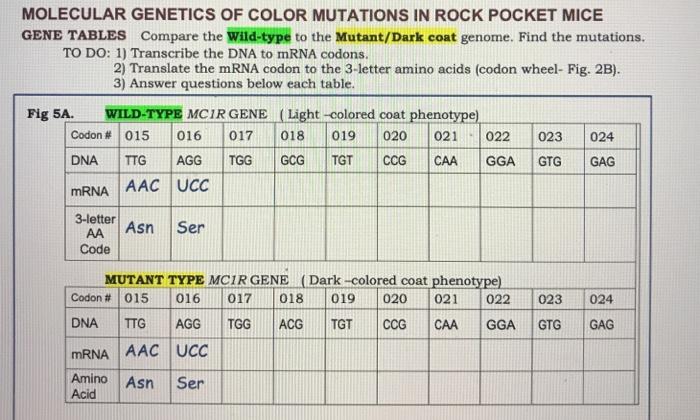
Molecular genetics techniques are used to study color mutations in pocket mice and other organisms. These techniques include:
- DNA sequencing: This technique is used to identify specific mutations in genes.
- Gene expression analysis: This technique is used to measure the expression levels of genes involved in color production.
- Genetic mapping: This technique is used to identify the location of genes responsible for color mutations.
FAQ Corner
What are the different types of color mutations in pocket mice?
Color mutations in pocket mice arise from various types of genetic alterations, including single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), insertions, deletions, and inversions.
How do color mutations affect the survival and reproduction of pocket mice?
Color mutations can impact survival and reproduction by altering camouflage, mate choice, and thermoregulation, influencing the fitness of individuals within different environments.
What techniques are used to study molecular genetics of color mutations in pocket mice?
Molecular techniques such as DNA sequencing, gene expression analysis, and genome-wide association studies are employed to identify and characterize the genetic basis of color mutations in pocket mice.
