Profit margins tend to be inversely related to inventory turns. – Profit margins tend to be inversely related to inventory turns, indicating a crucial relationship between efficient inventory management and business profitability. This concept underscores the significance of inventory optimization in driving financial success, and this article delves into the evidence and strategies behind this dynamic.
Understanding the inverse relationship between profit margins and inventory turns empowers businesses to make informed decisions regarding inventory management, ultimately enhancing profitability and overall financial performance.
Profit Margin Overview
Profit margins are financial ratios that measure the profitability of a business. They are calculated by dividing net income by revenue and expressed as a percentage. Profit margins are significant because they indicate how much profit a company generates for each dollar of revenue it earns.
Various factors influence profit margins, including operating costs, sales volume, and pricing strategies.
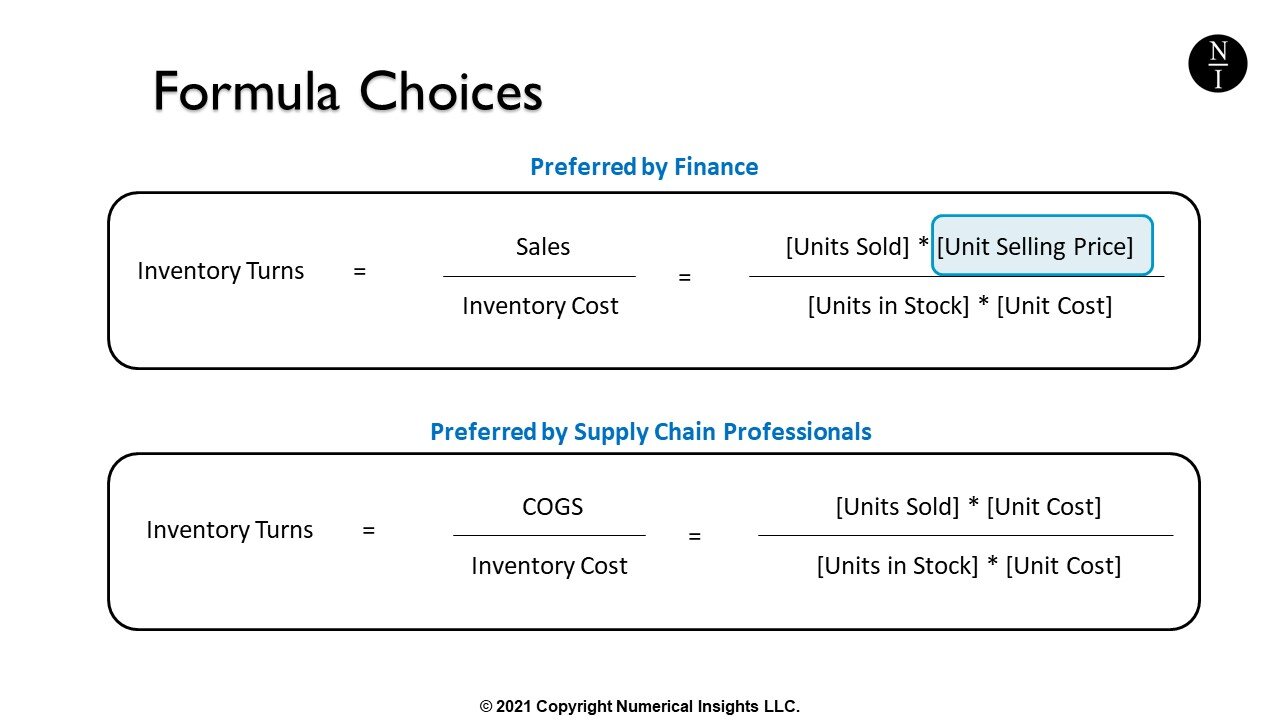
Inventory Turns Definition

Inventory turns is a metric that measures how efficiently a company manages its inventory. It is calculated by dividing the cost of goods sold by the average inventory over a specific period. Inventory turns indicate how many times a company’s inventory has been sold and replaced during that period.
Inverse Relationship between Profit Margins and Inventory Turns, Profit margins tend to be inversely related to inventory turns.
There is an inverse relationship between profit margins and inventory turns. This means that as inventory turns increase, profit margins tend to decrease, and vice versa. This relationship is supported by empirical evidence and can be explained by several underlying factors.
- Carrying costs:Higher inventory turns reduce the amount of time that inventory is held, which lowers the associated carrying costs, such as storage, insurance, and opportunity cost.
- Reduced obsolescence risk:Faster inventory turnover reduces the risk of inventory becoming obsolete or damaged, leading to lower losses and higher profit margins.
- Improved cash flow:Higher inventory turns free up cash that would otherwise be tied up in inventory, improving a company’s cash flow and overall financial health.
Consequences of High and Low Inventory Turns
High inventory turns can have positive consequences for profit margins by reducing carrying costs, obsolescence risk, and improving cash flow. However, excessively high inventory turns can also lead to stockouts and lost sales, which can negatively impact profitability.
Low inventory turns, on the other hand, can increase carrying costs, obsolescence risk, and reduce cash flow, all of which can lower profit margins. Additionally, low inventory turns may indicate inefficient inventory management practices, which can further reduce profitability.
Strategies to Optimize Profit Margins through Inventory Turns
Companies can implement several strategies to increase inventory turns and improve profit margins:
- Implement just-in-time (JIT) inventory management:JIT inventory management aims to minimize inventory levels by only ordering inventory when needed for production or sale.
- Improve inventory forecasting:Accurate inventory forecasting helps companies avoid overstocking or understocking, optimizing inventory levels and turns.
- Use technology to track inventory:Inventory management software and systems can help companies track inventory levels in real-time, identify slow-moving items, and optimize inventory turns.
- Outsource inventory management:Outsourcing inventory management to a third-party logistics (3PL) provider can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and increase inventory turns.
Impact of Inventory Management on Profitability
Effective inventory management practices contribute to higher profit margins by:
- Reducing carrying costs:Efficient inventory management minimizes inventory levels, lowering storage, insurance, and opportunity costs.
- Minimizing obsolescence risk:By maintaining optimal inventory levels, companies reduce the risk of inventory becoming obsolete or damaged, preventing losses and improving profitability.
- Improving cash flow:Efficient inventory management frees up cash tied up in inventory, improving cash flow and overall financial health.
- Optimizing inventory turns:Effective inventory management practices increase inventory turns, leading to improved profit margins as discussed earlier.
In addition, technology and data analytics play a significant role in optimizing inventory management. Advanced inventory management systems use data analytics to provide insights into inventory patterns, demand forecasting, and optimization strategies, enabling companies to make informed decisions and improve profitability.
Detailed FAQs: Profit Margins Tend To Be Inversely Related To Inventory Turns.
What is the significance of inventory turns in business operations?
Inventory turns measure the efficiency of inventory management, indicating how quickly inventory is sold and replaced. Higher inventory turns imply efficient inventory management, leading to lower holding costs and increased profitability.
How does effective inventory management contribute to higher profit margins?
Effective inventory management reduces inventory holding costs, such as storage, insurance, and obsolescence. Additionally, it prevents overstocking, which can lead to markdowns and losses due to outdated or damaged inventory.
What are some strategies to increase inventory turns and improve profit margins?
Strategies to increase inventory turns include implementing just-in-time inventory systems, improving demand forecasting, optimizing inventory levels, and reducing lead times through efficient supply chain management.
